Colorectal cancer, conjointly referred to as intestine cancer, carcinoma or body part cancer, is any cancer (a growth, lump, tumor) of the colon and therefore the body part. the planet Health Organization and Center for Disease Control and Prevention say it's the second most typical cancer worldwide, when carcinoma.
The yank Cancer Society suggests that regarding one in twenty individuals within the North American nationcan develop body part cancer throughout their lifespan, with the danger being slightly higher for men than for ladies. because of advances in screening techniques and enhancements in treatments, the death rate from body part cancer has been dropping for over twenty years.
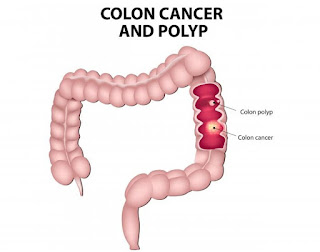
A body part cancer is also benign or malignant. Benign suggests that the growth won't unfold, whereas amalignance consists of cells that may unfold to alternative elements of the body and harm them.
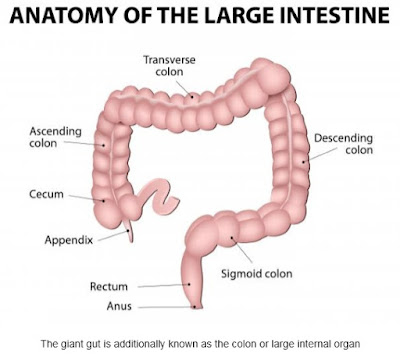
The colon and body part
The colon and body part belong to our body's systema alimentarium - along they're conjointly referred to as the big intestine.
The colon reabsorbs massive quantities of water and nutrients from undigested food merchandise as they pass onit.
The body part is at the top of the colon and stores excreta (stools, waste material) before being expelled from the body.
Symptoms of body part cancer
- Going to the bathroom a lot of usually.
- Diarrhea.
- Constipation.
- A feeling that the intestine doesn't empty properly when a laxation.
- Blood in excreta (stools).
- Pains within the abdomen.
- Bloating within the abdomen.
- A feeling of fullness within the abdomen (maybe even when not consumption for a while).
- Vomiting.
- Fatigue (tiredness).
- Inexplicable weight loss.
- A lump within the tummy or a lump within the back passage felt by your doctor.
- Unexplained iron deficiency in men, or in ladies when the climacteric.
As most of those symptoms might also indicate alternative attainable conditions, it's vital that the patient sees a doctor for a correct diagnosing. Anybody WHO experiences a number of these symptoms for four weeks ought tosee their doctor.
Causes of body part cancer
Experts say we have a tendency to aren't utterly positive why body part cancer develops in some individualsand not in others. However, many risk issues are known over the years - a risk factor are a few things which canincrease a personality's probabilities of developing a sickness or condition.
The attainable risk factors for body part factors are:
- Being older - the older you're the upper the danger is.
- A diet that's terribly high in animal supermolecule.
- A diet that's terribly high in saturated fats.
- A diet that's terribly low in dietary fiber.
- A diet that's terribly high in calories.
- A diet that's terribly high in alcohol consumption.
- Women WHO have had breast, ovary and womb cancers.
- A case history of body part cancer.
- Patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
- Being overweight/obese.
- Smoking. This study found that smoking is considerably related to associate degree accrued risk for body partcancer and death.
- Being physically inactive.
- Presence of polyps within the colon/rectum. Untreated polyps might eventually become cancerous.
- Having regional ileitis or Irritable intestine sickness have the next risk of developing body part cancer.
Most colon cancers develop among polyps (adenoma). These area unit usually found within the intestine wall.
How common is body part cancer?
 According to WHO (World Health Organization) body part cancer is that the second most typical growth amongeach men and ladies (after respiratory organ tumors).
According to WHO (World Health Organization) body part cancer is that the second most typical growth amongeach men and ladies (after respiratory organ tumors).
Approximately two of over 50-year-olds can eventually develop body part cancer in Western Europe.
40% of individuals WHO area unit diagnosed with body part cancer area unit already at a sophisticated stage of the cancer. For these patients surgery is perhaps the foremost probably possibility.
Colorectal cancer tends to have an effect on men and ladies equally. However, men tend to develop it at a younger age.
Tests and diagnosing for body part cancer
Screening will discover polyps before they become cancerous, moreover as police work carcinoma throughout its early stages once the possibilities of a cure area unit a lot of higher. the subsequent area unit the foremostcommon screening and diagnostic procedures for body part cancer:
Fecal occult biopsy (blood stool test)
This checks a sample of the patient's stool (feces) for the presence of blood. this will be done at the GP's (general practitioner's, medical aid physician's) workplace. However, most patients area unit given a kit that explains a way to take the sample reception. The patient then returns the sample to the doctor's workplace, and it's sent to a laboratory.
A blood diagnostic assay isn't 100 percent correct - it would not discover all cancers as a result of not all of them bleed. Even cancers that do bleed usually don't do thus all the time. Therefore, it's attainable that a patientincludes a negative result, although he/she has cancer. even though blood is detected, this could be caused byalternative diseases or conditions, like hemorrhoids. Some foods might recommend blood within the colon, onceactually, none was gift.
Stool desoxyribonucleic acid check
This check analyzes many desoxyribonucleic acid markers that colon cancers or malignant neoplasm polyps cells shed into the stool. Patients is also given a kit with directions on a way to collect a stool sample reception. This should be brought back to the doctor's workplace, and is then sent to a laboratory.
This check is far a lot of correct for police work carcinoma than polyps. However, it cannot discover alldesoxyribonucleic acid mutations which can indicate that a growth is gift.
Flexible flexible sigmoidoscopy
The doctor uses a endoscope, a flexible, slender and lighted tube, to look at the patient's body part and sigmoid (the colon is that the last of the colon, before the rectum). The check doesn't usually take quite many minutes and isn't painful; however can be uncomfortable. there's alittle risk of perforation of the colon wall. If the doctor detects a polyps or carcinoma he/she can then keep it up a endoscopy to look at the complete colon andconfiscate any polyps that area unit gift - they're going to then be examined beneath a magnifier.
A flexible sigmoidoscopy can solely discover polyps or cancer gift at the top third of the colon and therefore thebody part. If there area unit any in the other elements of the epithelial duct it'll not discover them.
Barium enema X-ray
Barium could be a distinction dye that's placed into the patient's intestine in associate degree irrigation type - it shows informed associate degree X-ray. during a double-contrast enema air is superimposed moreover. Themetal fills and coats the liner of the intestine, making a transparent image of the body part, colon, and infrequently of alittle a part of the patient's bowel. This procedure is commonly dole out at the side of a versatile flexible sigmoidoscopy to discover any tiny polyps the enema X-ray might have lost. If the enema X-ray detects something abnormal, the doctor might suggest a endoscopy.
Colonoscopy
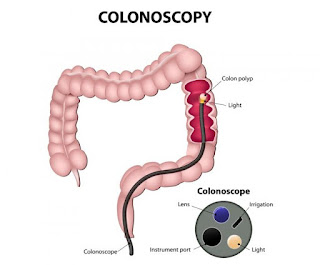 The doctor uses a endoscope, that is far longer than a endoscope. A endoscope could be a long, versatile and slender tube that is hooked up to a video camera and monitor. The doctor will see the complete of the colon andbody part. Any polyps discovered throughout this test may be removed there then - generally tissue samples (biopsies) is also taken instead. Taking biopsies doesn't hurt.
The doctor uses a endoscope, that is far longer than a endoscope. A endoscope could be a long, versatile and slender tube that is hooked up to a video camera and monitor. The doctor will see the complete of the colon andbody part. Any polyps discovered throughout this test may be removed there then - generally tissue samples (biopsies) is also taken instead. Taking biopsies doesn't hurt.
Although colonoscopies area unit painless, some patients area unit given a light sedative to calm them down. beforethe test the patient is also given an outsized quantity of laxative fluid to wash out the colon (enemas area unitseldom used). trauma and perforation of the colon wall area unit attainable complications, however extra ordinarily rare.
CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy)
A CT (computerized tomography) machine is employed to require pictures of the colon. The patient has to have a cleared colon for this test to be effective. even though something abnormal is detected, the patient can then wantstandard endoscopy. A study found that CT colonography might supply patients at accrued risk of body partcancer an alternate to endoscopy that's less-invasive, is better-tolerated and has smart diagnostic accuracy.
Ultrasound scan
Sound waves area unit accustomed facilitate show if the cancer has unfold to a different a part of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
This gives a three-dimensional image of the intestine and should facilitate the doctor in his/her diagnosing.
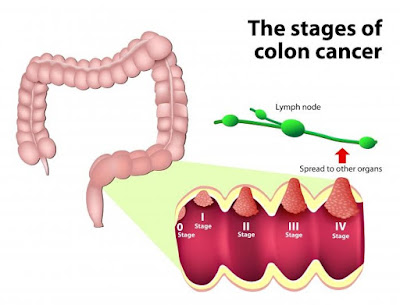
Staging the cancer
The stage of a cancer suggests that the extent of the cancer. As presently as a carcinoma diagnosing has beencreated the doctor can confirm its stage - this helps selected the foremost applicable treatment. The stages ofcarcinoma are:
- Stage zero (Also referred to as Duke A stage). - the earliest stage. it's still among the tissue layer (inner layer) of the colon or body part - conjointly known as cancer in place.
- Stage I (Also referred to as Duke B stage). - it's fully grown through the inner layer of the colon or body part,however has not nonetheless unfold on the far side the wall of the body part or colon.
- Stage II (Also referred to as Duke C stage). - it's fully grown through or into the wall of the colon or body part. However, it's not reached the near bodily fluid nodes nonetheless.
- Stage III (Also referred to as Duke D stage). - the near bodily fluid nodes are invaded by the cancer, however it'snot nonetheless affected alternative elements of the body.
- Stage IV (Also referred to as Duke E stage). - it's unfold to alternative elements of the body, as well as alternativeorgans, like the liver, the membrane lining the bodily cavity, lung, or ovary.
- Recurrent - the cancer has came back when treatment. it's going to return and have an effect on the body part, colon, or elsewhere within the body. Scientists have found that the presence of a biomarker in regional bodily fluidnodes is associate degree freelance predictor of sickness repeat in patients with body part cancer.
Treatments for body part cancer
The patient's treatment can rely upon many factors, as well as its size and placement, the stage of the cancer,whether or not or not it's repeated, and therefore the current overall state of health of the patient. a decentspecialist can justify all the treatment choices obtainable to the patient. this is often a chance for the patient toraise queries and acquire recommendation on life style changes which will facilitate recovery.
Treatment choices embrace therapy, radiation, and surgery:
Surgery for body part cancer
This is the foremost common body part cancer treatment. The affected malignant tumors and any bodily fluidnodes that area unit near are going to be removed. Surgeons take away bodily fluid nodes as a result of they'rethe primary place cancers tend to unfold to.
The intestine is typically seamed back along. On some occasions the body part might have to be taken oututterly - a ostomy bag is then hooked up for voidance. The ostomy bag collects stools and is usually placedbriefly - generally it's going to be a permanent live if it's unimaginable to affix up the ends of the intestine.
If the cancer is diagnosed early enough, surgery is also the sole treatment necessary to cure the patient body partcancer. even though surgery doesn't cure the patient, it'll ease the symptoms.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves employing a medication (chemical) to destroy the cancerous cells. it's ordinarily used forcarcinoma treatment. it's going to be used before surgery in a shot to shrink the growth. A study found that patients with advanced carcinoma WHO receive therapy and WHO have a case history of body part cancer have aconsiderably lower chance of cancer repeat and death.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy uses high energy radiation beams to destroy the cancer cells, and conjointly to forestall them from multiplying. This treatment is a lot of ordinarily used for body part cancer treatment. it's going to be used before surgery in a shot to shrink the growth.
Recovery from body part cancer
Malignant tumors can most likely grow and unfold to alternative elements of the body if left untreated. the possibilities of a whole cure rely staggeringly on however early the cancer is diagnosed and treated. A patient's recovery depends of the subsequent factors:
- The cancer stage once diagnosing was created.
- Whether a hole or blockage was created within the colon by the cancer.
- Whether the cancer has return.
- The patient's general state of health.
Prevention of body part cancer
We can do quite heap to lower our probabilities of developing body part cancer:
- Regular screenings - particularly if you have got had body part cancer before, you're over sixty, there's a case history of this kind of cancer, you have got regional ileitis. Some specialists say screening ought to beginwhen the age of fifty.
- Nutrition - check that your diet has many fiber, fruit, vegetables, and smart quality carbohydrates. Keep your consumption of white meat and processed meat right down to a minimum, or cut them out altogether. Switch from saturated fats to smart quality fats, like avocado, olive oil, fish oils, and nuts. However, this study found that thoughvegetarians have associate degree overall lower risk of developing cancers, their risk of developing body partcancer is more than meat eaters.
- Exercise - exercise frequently. Moderate, regular exercise has been shown to own a major impact on lowering a personality's risk of developing body part cancer.
- Bodyweight - keep your bodyweight healthy. Being overweight or weighty raises a personality's risk of developingseveral cancers, as well as body part cancer.
No comments:
Post a Comment